Case Study
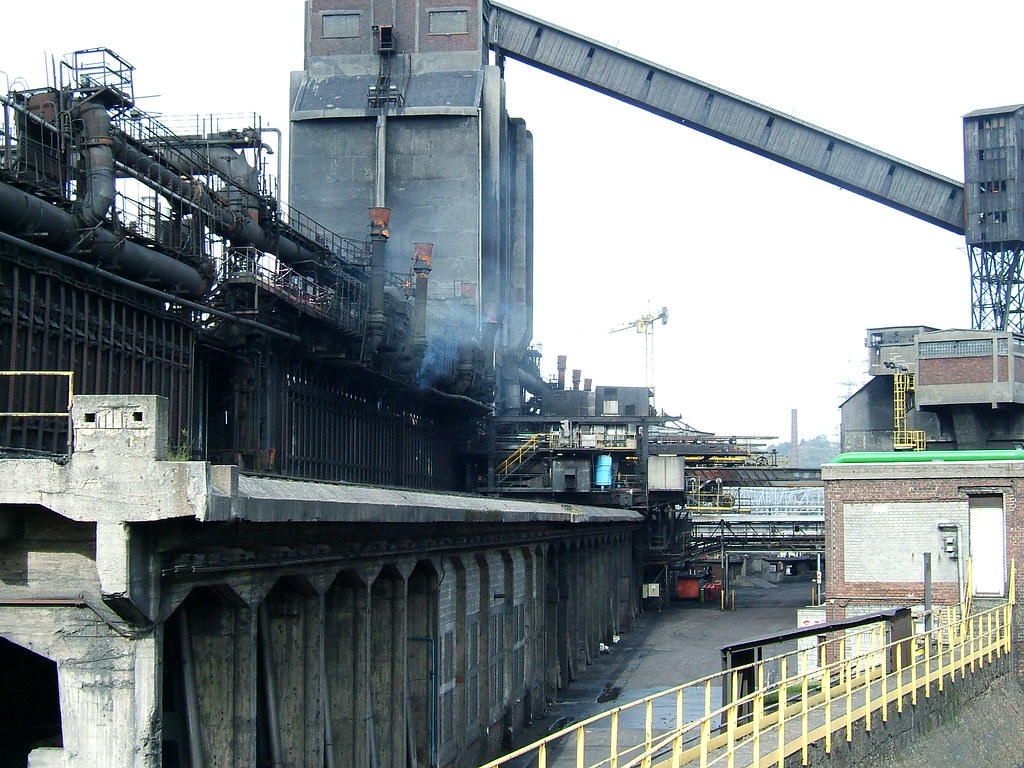
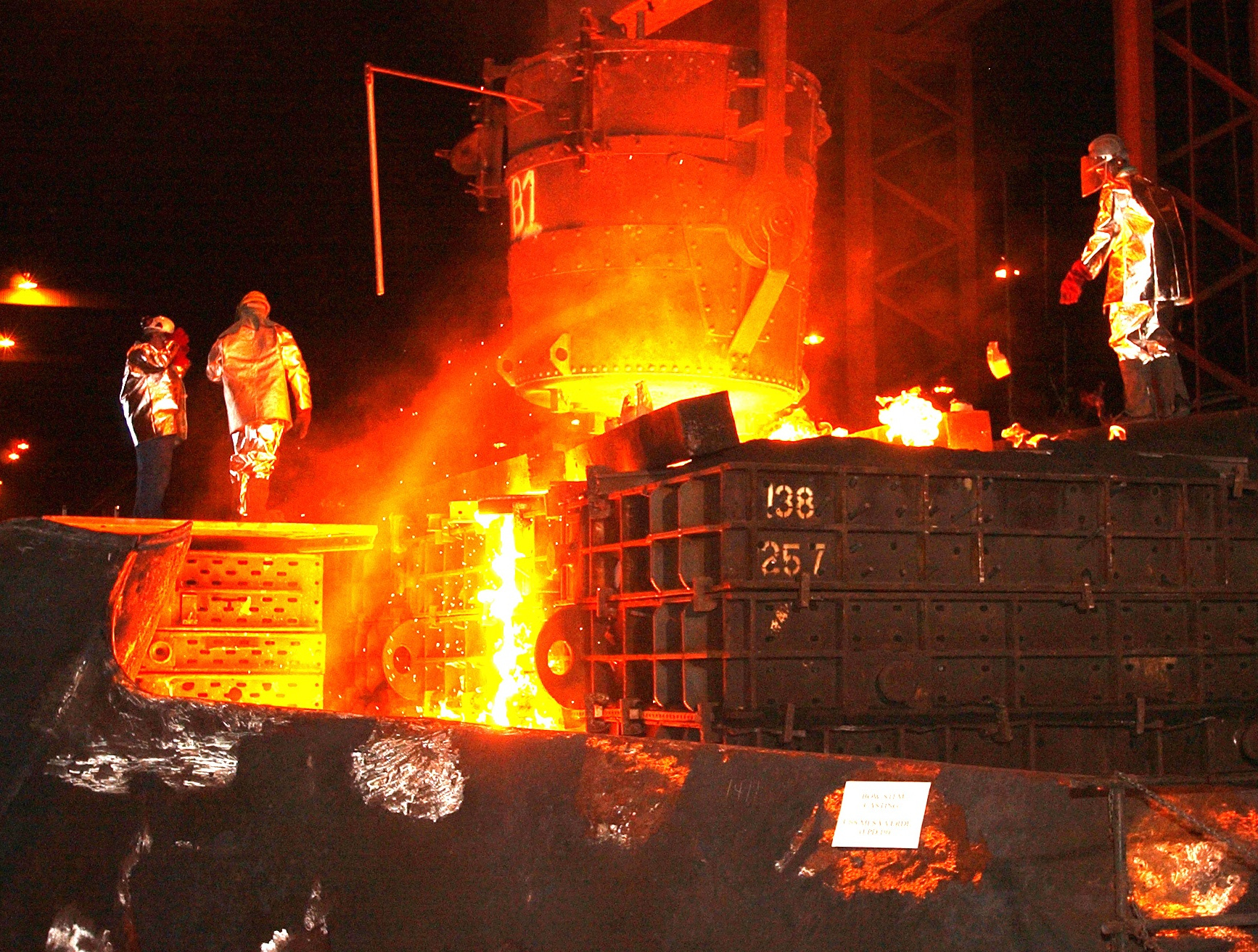
Typical water-cooled panels come with slag cups welded affixed to trap slag splash. The slag then sticks to the water panel surfaces. This action is viewed by operations as being a normal procedure for protecting the cooling tubes. However, the slag produced consists of a glass –metal mixture which allows heat band radiation to travel easily through their cross sections.
Problem: Whenever the water flow is not sufficient to cool the water tubing effectively, the slag does not stick, and this protection is lost. This is a significant problem, especially in the exhaust ports as the channeled hot dust is concentrated in the bends and curved sections. With roofs it is more troublesome, in that the roofs sometimes build up 6-20 inches of slag splatter. When swinging, the roof thermal shock of the adhered slag causes it to release, this material falls onto the hydraulic hoses and power lines, and sometimes the melt deck floor. In some cases, the roof panels adjacent to the electrodes, start arching, and this gouges holes which then releases water into the furnace bath. The procedure required to fixing this upset condition could result in stoppage of production.
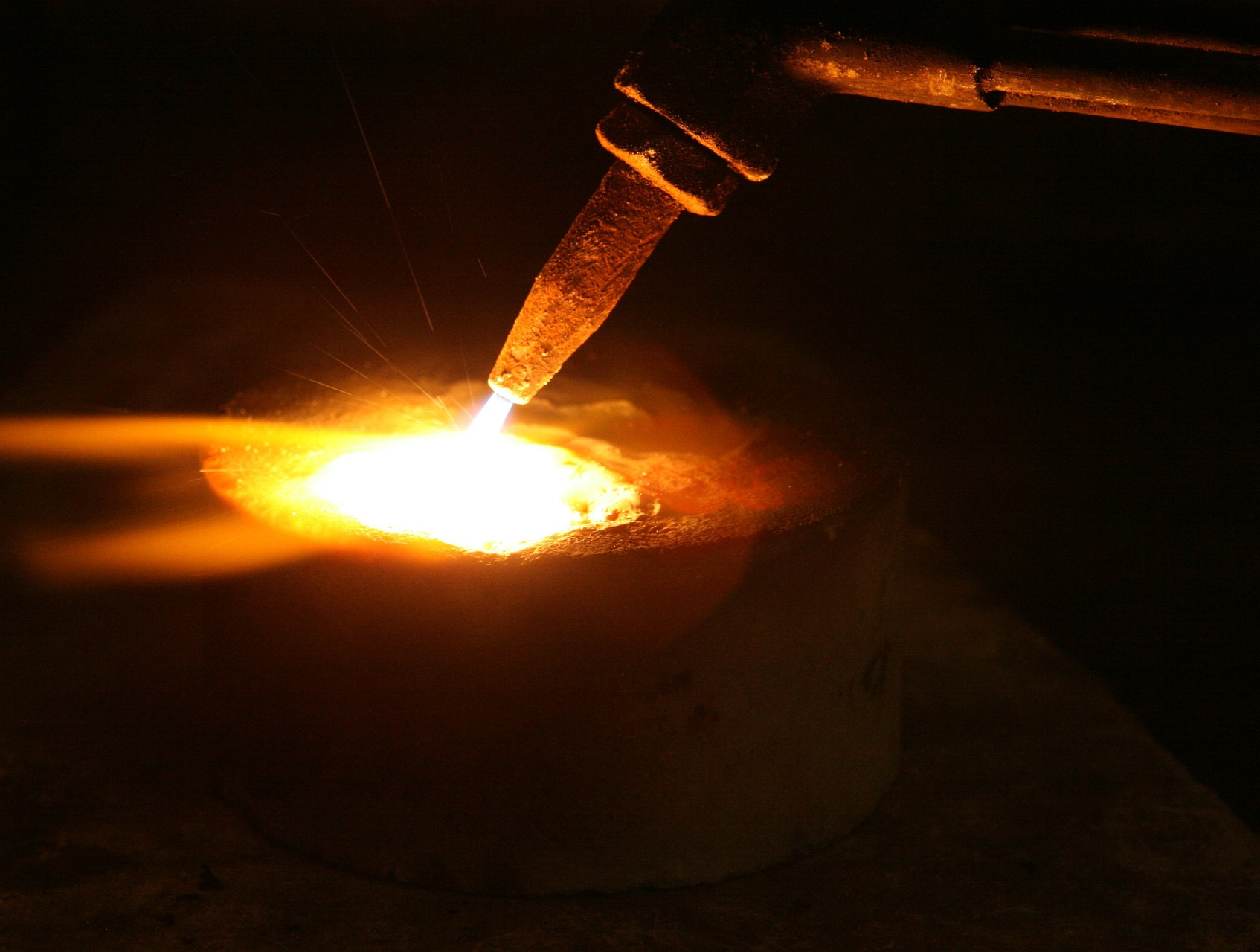
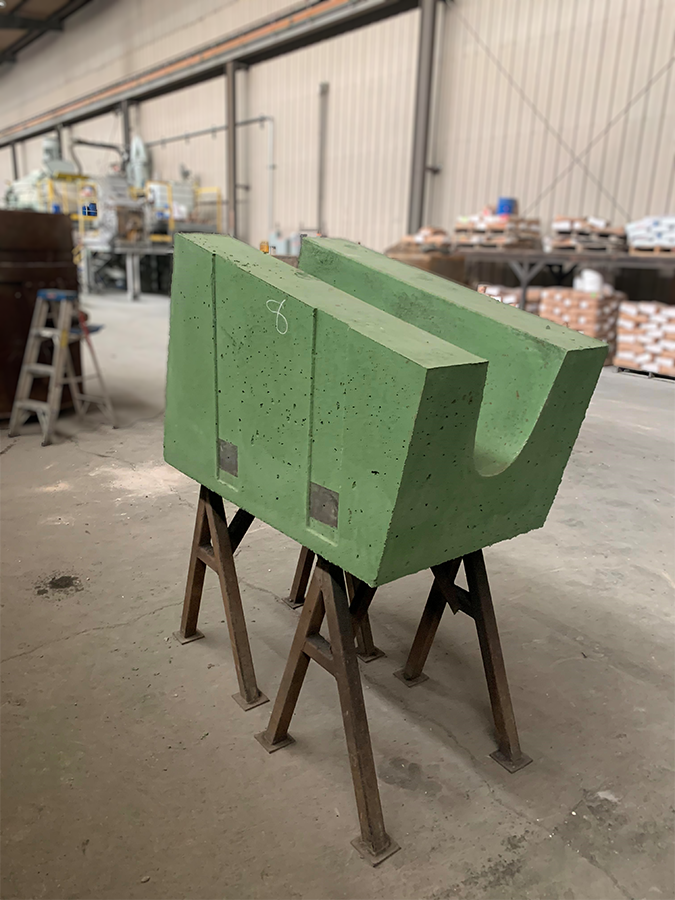
Solution: A typical electric arc furnace is ~ 60% efficient, with vast amounts of energy traveling unused into the water panels and into the air / dust exhaust-system. In slow down this inefficient energy escape, we install a layer of insulation, this is a far more efficient barrier than a slag covering. This slows down the inefficient energy escaping the system.
The benefits derived from using a refractory insulation barrier are:
- Reduces electrical costs per ton of molten steel.
- Reduces carbon footprint, by reducing electrical consumption.
- Increases production as reflective heating radiation, decreases melt times.
- Further increases production as unexpected furnace interruptions, due to leaking water panels
are eliminated. - Increases the safety for the operations, as leaking water can potentially create a hydrogen
explosion.
RENO has successfully employed RENO PIPE SHIELD CR for this application with outstanding success. This is a 190 pcf high alumina product that is colloidal-silica bonded. It has a temperature use limit of 2900°F. In addition, RENO PIPE SHIELD CR exhibits excellent thermal shock resistance critical in this application. Contact your RENO Representative for further information on this and other RENO Refractory products.